In the dynamic world of modern manufacturing, additive manufacturing has redefined the boundaries of what is possible in product design and production. Whether you are an industry professional seeking to deepen your understanding or a beginner for all things manufacturing, this guide will cover what additive manufacturing is, how it is used and its primary benefits.
A guide to additive manufacturing
November 6, 2023
By Annie Everill
What is additive manufacturing?
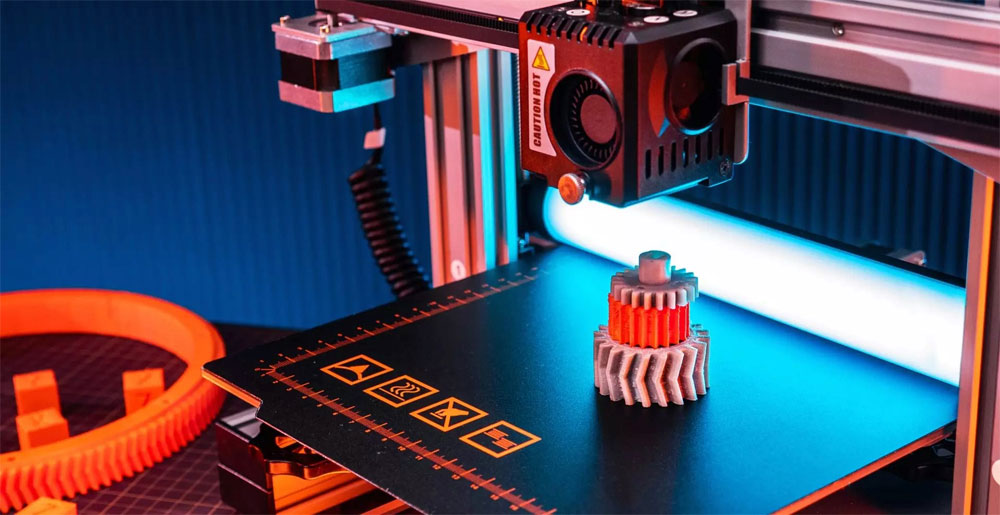
Additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as 3D printing, is a globally known manufacturing process that involves the design of three-dimensional objects by using layers. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away material from a solid block, additive manufacturing builds objects from the ground up.

Key principles
Layered Construction: Additive manufacturing begins with a digital 3D replica of the desired object. This method continuously adds thin cross-sections or layers to build a 3D result.
Diverse Materials: Depending on technology and printers, a selection of materials can be used within additive manufacturing including plastics, metals and ceramics.
Rapid Prototyping: Designers and engineers use additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping, enabling them to quickly create prototypes before committing to large-scale production. Find out more about rapid prototyping here.
Reduced Waste: Traditional manufacturing often generates significant material waste, however additive manufacturing is more material-efficient since it only uses the material necessary to build the object.
Customisation: This manufacturing solution is used in various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods, to create personalised products and components. This includes the creation of one-off goods.
Complex Assemblies: Some additive manufacturing techniques can produce complete assemblies of interconnected parts in a single printing process. This can reduce the need for assembly and improve the structural integrity of the final product.
Digital Control: This process is digitally controlled, from the initial 3D modelling to the printing itself. Meaning man-made input is less frequent. This allows for precise control and repeatability, allowing manufacturers to edit and change things remotely, without affecting the production line.
What are the benefits of additive manufacturing
Depending on business demands, additive manufacturing offers different benefits to different people, providing a more efficient solution to production management. Here are just a few of the main benefits additive manufacturing has to offer:
- Complex design and production
- Personalisation
- Rapid prototyping
- Reduced material waste
- Lower production costs
- On-demand production
- Lightweight structures
- Digital control and high-tech technologies
- Innovation
- Sustainability
What is the opposite of additive manufacturing?
The opposite of additive manufacturing is subtractive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing builds objects by layering, while subtractive manufacturing begins with a solid block and removes material from it until it achieves the desired part. Processes such as cutting, machining, milling, turning, drilling, and grinding can accomplish this removal of material.
